FastFlood Docs
Land Cover
Setting Mannings Surface Roughness Coefficient
The frictional force applied by the terrain on the flowing water depends on the type of cover on the terrain. This micro-scale process is captured well by Mannings surface friction coefficient in combination with the Darcy-Weisbach friction law for the Saint-Venant equations.
A Mannings coefficient of 0.01 scales the frictional force as it would be on a smooth surface (e.g. concrete, pavement, smooth bare surface). A value of 0.05 would be equivalent more to some types of cropland, while 0.15 would equate to dense forest with undergrowth.
As the velocities are determined by the Mannings Coefficient, the discharge response of a catchment is similarly influenced. Typically, higher Mannings values result in lower discharge peaks. On the other hand, locally, water can stagnate and build up higher depths due to a larger surface resistance.
Loading a Map
You can load a geoTIFF file containing Mannings surface roughness values. These can be derived from some land cover map, or just contain any value for each pixel. Note that there must be some non-zero and positive value for each pixel where the elevation model is defined. The elevation model functions as a mask, indicating where the model calculations are carried out.
Using Land Cover Information
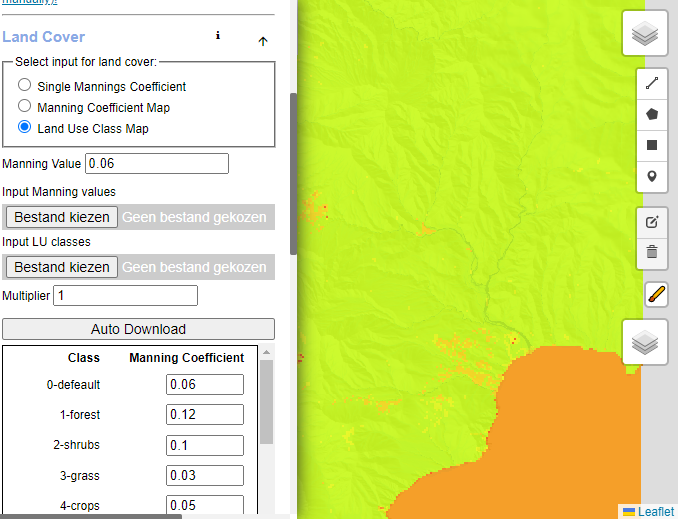
Land cover determines Mannings Surface roughness coefficient. It is therefore possible to upload a land cover class map, and determine Mannings coefficient values from an associated table. When loading the geoTiff file and selecting the class option, the file is automatically scanned for all class values, and a table is generated where you can fill in the Mannings values. You can save and load these tables from the export/import menu.
Typical values for Manning related to land use are:
- Bare – 0.01
- Roads – 0.01
- Grass – 0.03
- Dense shrubs – 0.11
- Dense forest – 0.15
- Cropland – 0.06
For more detailed information, see also the USGS Field manual for selecting Mannings Surface roughness coefficient, or the variety of tables published online.
## Automatically downloading land cover data
You can automatically download land cover data, with an associated Mannings N table. The data comes from the Copernicus WorldCover 10m dataset. This dataset contains 6 classes (bare, roads, grass, dense shrubs, dense forest, cropland). While the detail in classes is low, the spatial resolution typically enables sufficient detail for flood and hydrology simulations.